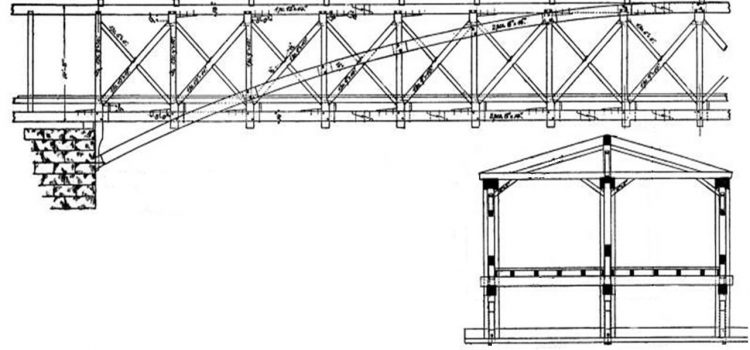
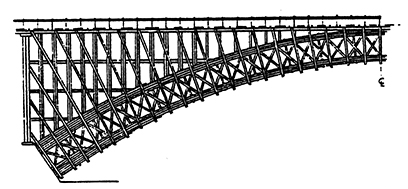
Abstract In 1850, the Bessemer converters were able to produce mass-production inexpensive steel. This technical advance was the key point that leaded to a suddenly extended use of steel in the bridge engineering field. Consequently, timber was pushed into the
Íñiguez G, Fernandez-Cabo JL, Fernandez-Cabo MC, Arriaga-Martitegui F, Majano-Majano A. (2010) Remarkable ancient timber bridges up to the 1850’s. Part I: general review. International Conference on Timber Bridges (ICTB-2010), Lillehammer, Norwey.