Axel Moço Martins, Erasmus student, ETSICCP
The Rance estuary, located in the north-west of France, has all the conditions to host a tidal plant to produce electricity for the neighboring towns.
Within these conditions, there are:
- Volumetric capacity of 184.000.000m3
- Distance of 750m between the two sides
- Tidal range of 13.50m
Then, in 1961, their construction began, with 33m wide dam that will house the power plant, a lock and a movable dam for 6 years until 1966.
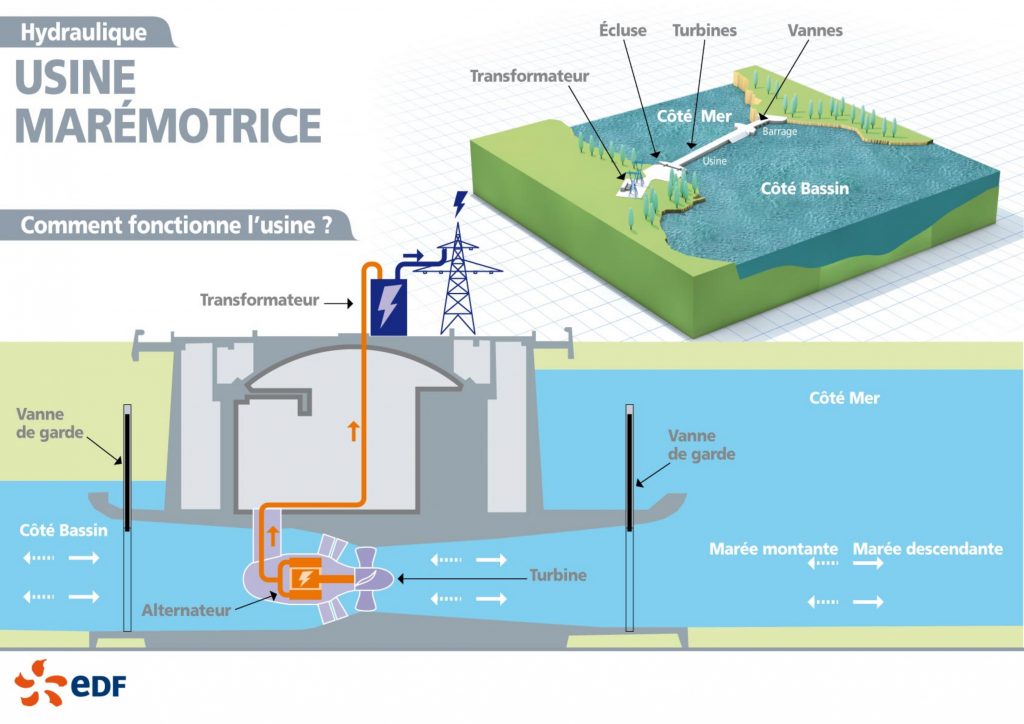
“Picture 1. Diagram of tidal plant operation (Source: Site EDF – https://www.edf.fr/sites/default/files/Hydraulique/Bretagne-Normandie/Documents/illustration_fonctionnement_rance.pdf)”
This civil work, which was interesting from the point of view of producing clean energy, turned out to be a catastrophe, impacting a large part of the estuary’s stakeholders: fauna, flora, or water with sedimentation effects.
FLORA:
Impact on riverbank vegetation:
Since the end of the construction of the dam, an impact on the vegetation located on the banks has been noticed. This is because the dam has created an artificial tide due to man’s need. So, the tidal range changed from 13.5m to 7m.
This means that all the vegetation that was previously flooded by the water is now no longer there, or is only there when the dam discharges (1): all the vegetation did not get used to this change and died.
Here we think, could this all have been thought of at the time of designing the dam?
One could think of an irrigation system for the vegetation, so work for the displacement of the vegetation downstream.
(1) Dam discharges: The valves are opened to create a current that reduces the volume of solid material deposited near the dam.
Impact on algae:
Eutrophication of the environment has led to the proliferation of green algae which also contributes to accelerated sedimentation of the watercourse, thus decreasing the flow per m3. The current has weakened and the temperature has increased, again leading to eutrophication.
FAUNA:
Impact on fish:
With the construction of the dam, we noticed a change on the fish population living in the waters.
First, a reduction in the quantity of fish with the disappearance of about 70% of the species living there before the construction, such as eels, flatfish or sandeels. If we speak of sandeel, the scientists explain this very negative disappearance for the waters of the estuary because its presence explains a quality of water.
One can now think that the quality of the water of the estuary is not good and it is necessary to intervene on this aspect.
Moreover, even with the disappearance of fish, according to scientists, there has been a balance of fish because, yes, some fish have disappeared, but there has been new colonization of fish, especially shellfish, which have settled on the seabed. This created a new fishing activity and developed the economic activity of the estuary.
Finally, the dam created a permeability of the estuary with a big problem on the circulation of fish. In fact, there are now two sides, the seaside, and the estuary side. So, the fish cannot move from one side to the other and they stay on the ground, which greatly affects their life status and their development. So, to find a solution so that the fish can move as it wants that fundamental, maybe to investigate on the left side with the lock.
SEDIMENTATION PROBLEMS:
In this part we will talk about the major problem of the estuary, which is the sedimentation that started around 1996, has lasted until now and, according to studies, will continue for the next few years.

Picture 2. Illustration of the effect of sedimentation in the estuary (Source: http://www.geographie.ens.fr/l-envasement-de-l-estuaire.html”)
Why?
The construction impacted the tidal range, the speed of the currents, which decreased. Over time the morphology of the estuary has changed leading to this effect.
Consequences?
First, boating is the activity that was most impacted by the change in currents.
Bathing is also affected with the presence of silt instead of sandy beaches. Swimming possibilities are limited and the danger of sinking in the silt is limited.
Change also in the landscape which is noticed by the inhabitants who see their visual environment changing. The estuary is filling in with silt and becoming a wet landscape.
Limitation methods:
So, like every problem, solutions must be found. This is what was done with the work of the association C.O.E.U.R (2), and EDF (3) working together to remove all this sedimentation.
– First solution: dam discharges, done since 1966 by EDF.
– Second solution: dredging, which consists with a specialized boat, injecting water under pressure to create a current in the sediment banks and create their movement.
– Third solution: sediments trap, with a capacity of 63,000m3, an idea largely led by the association which consists in creating a zone which will collect all the sediments withdrawn from the estuary. A great success, but with all the volume of sediments in the estuary it is necessary to build others.
(2) C.O.E.U.R: association that fights for the good management of the estuary.
(3) EDF: electricity supplier in France, is the concessionaire of the power plant.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the power plant, besides proposing clean energy for the region, brought many environmental problems to the estuary, which are not negligible.
From my point of view, this project should have been better studied with all the possible environmental impacts.
Now, for me, it would be impossible to design such a dam with all the problems it generates, money, time, and equipment expenses.
And you, do you think this project would have seen the light of day today?
Sources:
[1] Geoffroy CAUDE, Gestion sédimentaire de l’estuaire de la Rance, report, https://www.economie.gouv.fr/files/files/directions_services/cge/estuaire-rance.pdf
[2] EDF, L’usine marémotrice de la Rance, site web, https://www.edf.fr/usine-maremotrice-rance/presentation
[3] ENS, Saint-Malo, site web, http://www.geographie.ens.fr/l-envasement-de-l-estuaire.html
